Geographic Information System (GIS) | GIS Technology 2024-25
Contents
Geographic Information System (GIS)
Geographic Information System (GIS) is a powerful tool for mapping and analyzing locations, combining data from multiple sources. This technology is essential for various applications, including urban planning, disaster management, and natural resource management. GIS helps visualize spatial information, identify patterns, and understand relationships, making it indispensable for modern geography and environmental studies. From navigation to business logistics, GIS is integrated into everyday use.

Key Components of GIS
- Spatial Data: Information tied to geographic locations, such as coordinates (latitude and longitude) or addresses.
- Attribute Data: Descriptive information associated with spatial features, stored in databases linked to spatial data.
- Software: Tools and applications used to process and analyze spatial data, such as mapping software.
- Hardware: Computers and devices used to run GIS software and store data.
- People: GIS professionals who analyze data, create maps, and develop applications for various purposes.
- Layers: Different themes of geographic data systematically mapped and maintained.
Common Layers in National Mapping Systems
- Administrative Boundaries: National borders and political divisions.
- Transportation Networks: Roads, highways, railways, and airports.
- Hydrography: Rivers, lakes, and coastlines.
- Topography: Elevation, landforms, and digital elevation models (DEMs).
- Land Use and Land Cover: Residential, commercial, industrial areas, and vegetation types.
- Utilities and Infrastructure: Power lines, water pipelines, and communication infrastructure.
- Cultural and Built Environment: Buildings, monuments, and protected areas.
- Geological and Natural Resources: Fault lines, mineral deposits, and renewable energy sources.
- Population and Demographics: Population density and demographic data.
- Environmental and Ecological Data: Ecoregions and environmental quality monitoring.
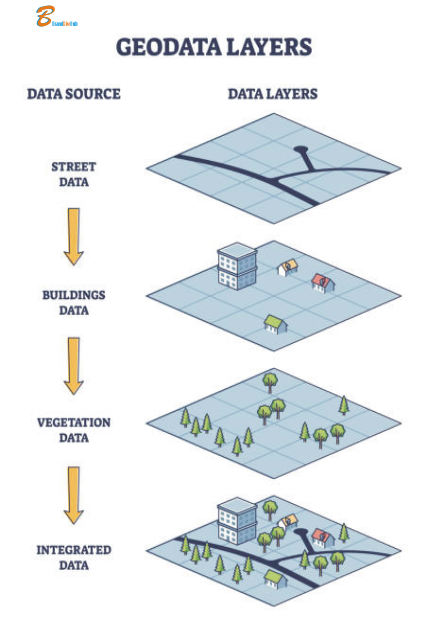
Power of Geographic Information Systems (GIS)
In today’s data-driven world, Geographic Information Systems (GIS) have emerged as a transformative technology. They revolutionize how we understand and interact with spatial data. GIS is a framework for gathering, managing, and analyzing data rooted in the science of geography. It integrates various data types. It applies spatial location to provide deeper insights into patterns and relationships. This capability is invaluable across numerous industries.
Applications of GIS
- Urban Planning: Analyzing urban growth, planning infrastructure, and managing urban services.
- Environmental Management: Monitoring ecosystems, managing natural resources, and analyzing ecological impacts.
- Transportation: Supporting route planning, traffic management, and infrastructure development.
- Healthcare: Disease tracking, resource allocation, and health outcome analysis.
- Emergency Management: Disaster response planning, risk assessment, and recovery efforts.
Benefits of GIS
- Enhanced Decision Making: Provides a spatial context that enhances understanding and supports better decisions.
- Data Integration: Integrates various types of data for comprehensive analysis and richer insights.
- Improved Communication: Maps and visualizations help communicate complex information clearly.
- Increased Efficiency: Automates data collection and analysis processes, saving time and reducing costs.
Future of GIS
The future of GIS is bright, with technological advancements driving new applications and capabilities. Innovations in AI, machine learning, and real-time data processing are set to enhance the potential of GIS. They will make it an even more powerful tool for spatial analysis. These advancements will aid in decision-making.
FAQs
Q1: What is a Geographic Information System (GIS)?
Answer: A Geographic Information System (GIS) combines hardware, software, and data to capture, manage, analyze, and display geographically referenced information. By linking data to maps, GIS helps visualize, question, analyze, and interpret spatial data, revealing relationships, patterns, and trends.
Q2: How is GIS used in urban planning?
Answer: In urban planning, GIS analyzes urban growth, plans infrastructure, and manages services. Planners assess land use patterns and design transportation systems. They optimize public service delivery. They also engage communities through interactive maps and visualizations. This approach supports informed decision-making and efficient resource allocation.
Q3: What industries benefit the most from GIS technology?
Answer: GIS technology benefits various industries, including:
- Environmental Management: Monitoring ecosystems, managing natural resources, and assessing impacts.
- Transportation: Route planning, traffic management, and infrastructure development.
- Healthcare: Disease tracking, resource allocation, and health outcome analysis.
- Emergency Management: Disaster response planning, risk assessment, and recovery efforts.
- Real Estate: Property analysis, market trend assessment, and site selection.
Q4: What are the main components of a GIS?
Answer: The main components of a GIS include:
- Hardware: Physical devices (computers, servers, GPS devices) running GIS software.
- Software: Applications for processing, analyzing, and visualizing spatial data (e.g., ArcGIS, QGIS).
- Data: Geographically referenced data, including maps, satellite imagery, and databases.
- People: GIS analysts, urban planners, and environmental scientists designing, managing, and using GIS applications.
- Methods: Procedures and techniques for collecting, analyzing, and interpreting spatial data.
Q5: How does GIS improve decision-making?
Answer: GIS improves decision-making by providing a spatial context to data, enhancing understanding and insights. It integrates various data types, making analysis comprehensive. Visualizing data on maps helps identify patterns and trends. These patterns and trends are not easily seen through traditional analysis. This leads to more informed decisions in planning, resource management, and problem-solving.
Conclusion
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) are crucial for solving complex problems and making informed decisions across various domains. GIS technology will continue to evolve. Its applications will expand. This evolution will further unlock the power of spatial data to drive progress and innovation.








Hey there,
Premium Deals Await You
LV, Gucci, Coach, Nike, Air Jordan, Oakley, Rayban, and Armani at over 90% off. Visit https://luxesource.shop today.
Enjoy,
Tod