Powerful Electronics Insights | Transform Your Knowledge for 2025
What are Definition and Meaning of Powerful Electronics Insights? It’s all about the things that power things, like the secret sauce in your gadgets, making them tick. When you flip a switch or a plug in your phone, that’s electronics at work. It’s all about wires, chips, and getting things done without you realizing it. So while you cling to your favorite device, remember that it’s all thanks to the definition and meaning of electronics.
Contents
Understanding Definition and Meaning of Powerful Electronics Insights: Exploring the Basics
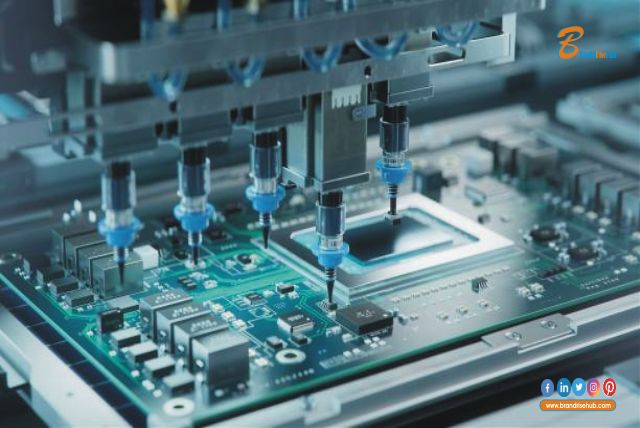

Definition and Meaning of Powerful Electronics Insights describes a field of study. It involves understanding and applying electrical circuits. It includes components like transistors, diodes and integrated circuits. They are used to make devices and systems that run on electricity. Electronics is about making things work with electrical power.
- Electricity: At the core of electronics is the concept of electricity. Electricity refers to the flow of electric charge through conductive materials such as wires. It is produced in several ways. These include chemical reactions (as in batteries), electromagnetic induction (as in generators), and the photoelectric effect (as in solar cells). All of these are fundamental components.
- Circuits: A circuit is a closed loop through which an electric current can flow. It typically consists of components. These include resistors, capacitors, inductors, and semiconductor devices. They are connected by conductive wires or traces on a circuit board. Circuits can be categorized into analog and digital circuits based on the type of signals they process.
- Components: Electronics components are the building blocks of electronic circuits. Some common components include resistors. They restrict the flow of current. Capacitors store electrical energy. Inductors store magnetic energy. Diodes allow current to flow in one direction. Transistors amplify or switch electronic signals.
- Semiconductor Devices: Semiconductor devices, particularly transistors and diodes, play a crucial role in modern electronics. Transistors serve as amplifiers, switches, and signal processors. Diodes allow current to flow in one direction. This enables rectification and signal modulation.
- Integrated Circuits (ICs): Integrated circuits, or ICs, are miniature electronic circuits fabricated on a semiconductor material (usually silicon). They consist of thousands to billions of individual components. These include transistors, resistors, and capacitors, which are all etched onto a tiny chip. ICs have revolutionized electronics by enabling the creation of complex electronic systems in compact and efficient form factors.
- Digital Electronics: Digital electronics deals with signals that have discrete levels. They are typically represented as 0 and 1. These systems process information using logic gates. It forms the foundation of modern computing, telecommunications, and information technology.
- Analog Electronics: Analog electronics, on the other hand, deal with signals that vary continuously over time. It is essential for tasks such as amplification, modulation, and signal processing in audio and radio frequency applications.
What is Powerful Electronics Insights?
Definition and Meaning of Electronics is about studying, designing, and using gadgets and systems that use electricity to do things. You know, like making things work, sending messages, storing information, or moving things around. It’s like playing with electricity to make things happen.
Definition and Meaning of Electronics? It’s all about controlling and playing with electrical signals using small parts like resistors, capacitors, and transistors. These small pieces are put together to form circuits. They can be simple or very complex, depending on what you are making. Simply put, electronics is about tinkering with electricity.
Electronics encompasses a wide range of applications, including:
- Consumer Electronics
- Communications
- Control Systems
- Medical Electronics
- Power Electronics
- Embedded Systems
The Fundamentals of Electronics

The fundamentals of electronics encompass several key concepts that form the foundation of understanding how electronic devices and systems operate. Here’s an overview of some fundamentals:
- Electricity
- Voltage, Current, and Resistance
- Circuits
- Components
- Semiconductor Devices
- Analog and Digital Electronics
- Integrated Circuits (ICs)
Key Components of Electronics Systems
Electronic systems consist of various components that work together to perform specific functions. Here are some key components commonly used in electronic systems:
- Power Supply: The power supply provides electrical energy to the system. It converts input power from sources such as batteries, mains electricity, or renewable energy sources. This is transformed into the appropriate voltage and current levels required by the system’s components.
- Microcontroller/Microprocessor: These are programmable integrated circuits (ICs) that serve as the brains of the electronics system. Microcontrollers are typically used in embedded systems and provide processing power for controlling and interacting with other components. Microprocessors are more powerful and are commonly used in computing devices.
- Sensors: Sensors detect physical properties or environmental conditions and convert them into electrical signals. There are various types of sensors, including temperature sensors, pressure sensors, motion sensors, proximity sensors, and light sensors. Sensors are essential for gathering data and enabling interaction with the external environment.
- Actuators: Actuators are devices that convert electrical signals into mechanical motion or other physical actions. Common types of actuators include motors, solenoids, relays, and valves. Actuators are used to control various mechanisms, such as moving parts, opening and closing valves, and triggering alarms.
- Displays: Displays are output devices that present information visually to the user. Common types of displays include liquid crystal displays (LCDs) and light-emitting diode (LED) displays. Other types are organic light-emitting diode (OLED) displays and e-ink displays. Displays are used for presenting text, images, videos, and other visual content.
- Memory: Memory components store data and program instructions for the system to access when needed. There are different types of memory. Random-access memory (RAM) is used for temporary storage. Read-only memory (ROM) is used for permanent storage of firmware and boot code.
- Communication Interfaces: Communication interfaces enable the system to communicate with external devices, networks, or users. Examples of communication interfaces include serial ports, USB ports, Ethernet ports, Wi-Fi modules, Bluetooth modules, and radio frequency (RF) transceivers.
- Integrated Circuits (ICs): Integrated circuits are miniature electronic circuits fabricated on a semiconductor material (usually silicon). They can contain thousands to billions of individual components on a tiny chip. These components include transistors, resistors, and capacitors. ICs provide various functions, such as amplification, signal processing, voltage regulation, and digital logic operations.
Definition and Meaning of Powerful Electronics Insights: Shapes Our World
Electronics play a pervasive and transformative role in shaping our world across various domains.
1. Communication: Electronics revolutionized communication by enabling instantaneous and global connectivity. Electronic communication technologies have facilitated the exchange of information. They have also enabled the exchange of ideas and culture on an unprecedented scale. This occurs through mediums like telephones to smartphones, email to social media, and satellites to the internet.
2. Information Technology: The advent of computers and digital electronics has transformed the way we store, process, and access information. Electronics power the infrastructure from personal computers and servers to cloud computing and data centers. They drive modern information technology. This enables tasks such as data analysis, artificial intelligence, and machine learning.
3. Entertainment: Electronics have revolutionized entertainment industries, including television, film, music, gaming, and virtual reality. High-definition displays and surround sound systems enhance viewing and listening experiences. Streaming services and video games offer interactive entertainment. Electronic devices and technologies provide immersive and interactive entertainment experiences.
4. Transportation: Electronics have enhanced safety, efficiency, and convenience in transportation systems. Automotive electronics such as engine control units and anti-lock braking systems are crucial. Navigation systems and advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) also play an important role in modern vehicles. Additionally, electronic fare collection systems, traffic management systems, and public transportation infrastructure contribute to efficient and sustainable transportation networks.
5. Healthcare: Electronics have revolutionized healthcare by enabling advancements in medical imaging, diagnostics, treatment, and patient monitoring. From X-ray machines and MRI scanners to pacemakers and insulin pumps, electronic medical devices improve diagnosis, therapy, and patient outcomes. Wearable devices, telemedicine platforms, and health monitoring apps empower individuals to track and manage their health proactively.
6. Energy: Powerful Electronics Insights contribute to energy generation, distribution, and consumption. This includes renewable energy systems, smart grids, and energy-efficient technologies. Solar panels, wind turbines, and battery storage systems harness renewable energy sources. Electronic controls and sensors optimize energy usage. They also reduce wastage in buildings, appliances, and industrial processes.
7. Manufacturing and Automation: Electronics enable automation and robotics in manufacturing processes, enhancing productivity, precision, and scalability. Programmable logic controllers (PLCs), industrial robots, and sensors automate repetitive tasks. Machine vision systems and artificial intelligence optimize quality control. They also enhance production efficiency.
8. Environmental Monitoring and Conservation: Electronics facilitate environmental monitoring. They also support conservation and sustainability efforts. This is achieved through sensors, remote sensing technologies, and data analytics. Electronic systems offer valuable insights for environmental management. These insights come from weather monitoring stations, air quality sensors, satellite imagery, and ecological modeling.
Electronics shape our world in diverse ways, driving innovation, connectivity, efficiency, and advancements across sectors and industries. As electronic technologies continue to advance, they will address global challenges. They will also improve the quality of life for people around the world. Electronics will gain a lot of popularity in the coming۔
Summing Up
Meaning of electronics? The gadgets we can’t live without? From our phones to hospital supplies, electronics are the backbone of our daily grind. They’re all about connecting us, making things better, and making life easier. With bits like microcontrollers and sensors, that’s why we’re always plugged in, always connected.
They seem to have the power to change how we do things. This could be talking to someone across the world. It could also mean hitting our hearts just right. And they are also the ones pushing us towards a greener, better future. So Electronics? It is the heartbeat of our modern world.








One Comment